
Physics, 02.02.2021 07:10 paris4ever23
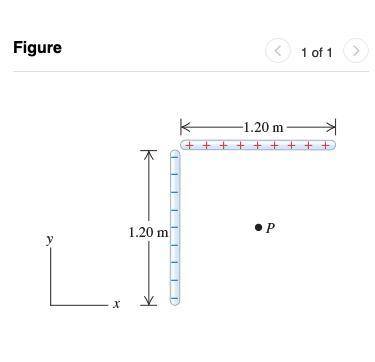
Two 1.20 m nonconducting rods meet at a right angle. One rod carries +1.90 μC of charge distributed uniformly along its length, and the other carries -1.90 μC distributed uniformly along it (Figure 1).
Part A
Find the magnitude of the electric field these rods produce at point P
, which is 60.0 cm from each rod.
Part B
Find the direction angle of the electric field from part A. The angle is measured from the +x
-axis toward the +y-axis.

Answers: 3


Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 15:00
The simple interest on a loan of $200 at 10 percent interest per year is $10 per year until the loan is paid off. $15 per year until the loan is paid off. $20 per year until the loan is paid off. $25 per year until the loan is paid off.
Answers: 2

Physics, 21.06.2019 18:10
How does the space charge width change with forward and reverse bias? also, calculate the space charge width for a reverse bias of 4v on a silicon pn junction at t = 300k and doping concentrations of na = 5x1015cm-3 , nd = 5x 1016 cm-3 .
Answers: 3

Physics, 21.06.2019 22:00
In 1980, alfa romeo introduced the first system to smooth a rough idle caused by ignition and camshaft timing changes.
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 07:30
Some material consisting of a collection of microscopic objects is kept at a high temperature. a photon detector capable of detecting photon energies from infrared through ultraviolet observes photons emitted with energies of 0.3 ev, 0.5 ev, 0.8 ev, 2.0ev, 2.5ev, and 2.8ev. these are the only photon energies observed. (a) draw and label a possible energy-level diagram for one of the microscopic objects, which has four bound states. on the diagram, indicate the transitions corresponding to the emitted photons. explain briefly. (b) would a spring–mass model be a good model for these microscopic objects? why or why not? (c) the material is now cooled down to a very low temperature, and the photon detector stops detecting photon emissions. next, a beam of light with a continuous range of energies from infrared through ultraviolet shines on the material, and the photon detector observes the beam of light after it passes through the material. what photon energies in this beam of light are observed to be significantly reduced in intensity (“dark absorption lines”)? explain briefly.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Two 1.20 m nonconducting rods meet at a right angle. One rod carries +1.90 μC of charge distributed...
Questions



Mathematics, 26.05.2021 01:00

Physics, 26.05.2021 01:00


Mathematics, 26.05.2021 01:00







Mathematics, 26.05.2021 01:00





Mathematics, 26.05.2021 01:00





