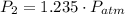To determine the pressure in a fluid at a given depth with the air-filled cartesian diver, we can employ Boyle's law, which states that the pressure in an ideal gas (held at constant temperature) is inversely proportional to its volume. At a fluid's surface, the pressure of the fluid is the same as the pressure of the atmosphere just above it, which we'll denote as LaTeX: P_{atm}P a t m. If the volume of air, which can be treated as an ideal gas here, in the cartesian diver decreases by 19% as it is lowered to a specific depth in the fluid, the pressure of the fluid at this depth, in terms of atmospheric pressure, is

Answers: 1


Another question on Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 07:30
Write the function getkthdigit(n, k) that takes a possibly-negative int n and a non-negative int k, and returns the kth digit of n, starting from 0, counting from the right
Answers: 3


Physics, 22.06.2019 13:40
An ideal otto cycle has a compression ratio of 10.5, takes in air at 90 kpa and 40°c, and is repeated 2500 times per minute. using constant specific heats at room temperature, determine the thermal efficiency of this cycle and the rate of heat input if the cycle is to produce 90 kw of power.
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 16:30
If anyone who can me with this hw? i would really appreciate it
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
To determine the pressure in a fluid at a given depth with the air-filled cartesian diver, we can em...
Questions


Mathematics, 11.02.2021 20:30


English, 11.02.2021 20:30



Chemistry, 11.02.2021 20:30







History, 11.02.2021 20:30

Mathematics, 11.02.2021 20:30

Mathematics, 11.02.2021 20:40




Biology, 11.02.2021 20:40

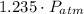 .
.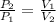 (1)
(1)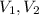 - Initial and final volume.
- Initial and final volume.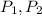 - Initial and final pressure.
- Initial and final pressure.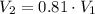 , then the pressure ratio is:
, then the pressure ratio is: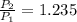
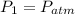 , then the final pressure of the gas is:
, then the final pressure of the gas is: