
Physics, 12.08.2020 04:01 scavalieri3746
Warm blooded animals are homeothermic; that is, they maintain an approximately constant body temperature. (Forhumans it's about 37 oC.) When they are in an environment that is below their optimum temperature, they use energy derived from chemical reactions within their bodies to warm them up. One of the ways that animals lose energy to their environment is through radiation. Every object emits electromagnetic radiation that depends on its temperature. For very hot objects like the sun, that radiation is visible light. For cooler objects, like a house or a person, that radiation is in the infrared and is invisible. Nonetheless, it still carries energy. Other ways that energy is lost by a warm animal to a cool environment includes conduction (direct touching of a cooler object) and convection (cooler air moving and carrying thermal energy away). See Heat Transfer for a discussion of all three.
For this problem, we'll just consider how much energy an animal needs to burn (obtain from internal chemical reactions) in order to stay warm just from radiation losses. The rate at which an object loses energy through radiation is given by the Stefan-Boltzmann equation:
Rate of energy loss = AεσT4
where T is the absolute (Kelvin) temperature, A is the area of the object, ε is the emissivity (unitless and =1 for a perfect emitter, less for anything else), and σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant:
σ = 5.67 x 10-8 J/(s m2 K4)
Consider a patient trying to sleep naked in a cool room (55 oF = 13 oC). Assume that the person being considered is a perfect emitter and absorber of radiation (ε = 1), has a surface area of about 2.5 m2, and a mass of 80 kg.
a. A person emits thermal radiation at a rate corresponding to a temperature of 37 oC and absorbs radiation at a rate (from the air and walls) corresponding to a temperature of 13 oC. Calculate the individual's net rate of energy loss due to radiation (in Watts = Joules/second).
net rate of energy loss = Watts
b. Assume the patient produces no energy to keep warm. If they have a specific heat about equal to that of water (1 Cal/kg-oC) how much would their temperature fall in one hour? (1 Cal = 1kcal = 103 cal)
ΔT = oC
c. Given that the energy density of fat is about 9 Cal/g, how many grams of fat would the person have to utilize to maintain their body temperature in that environment for one hour?
amount of fat needed = g

Answers: 2


Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 21:30
Aparticle with mass 1.81×10−3 kg and a charge of 1.22×10−8 c has, at a given instant, a velocity v⃗ =(3.00×104m/s)j^. what are the magnitude and direction of the particle’s acceleration produced by a uniform magnetic field b⃗ =(1.63t)i^+(0.980t)j^?
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 12:30
Compare the horizontal displacement of the two balls as they travel to the ground. what do you observe?
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 14:20
A1-lb collar is attached to a spring and slides without friction along a circular rod in a vertical plane. the spring has an undeformed length of 5 in. and a constant k =25 lb/ft. knowing that the collar is released from being held at a determine, the speed of the collar and the normal force between the collar and the rod as the collar passes through b.
Answers: 3

You know the right answer?
Warm blooded animals are homeothermic; that is, they maintain an approximately constant body tempera...
Questions


History, 27.10.2019 14:43

English, 27.10.2019 14:43






Mathematics, 27.10.2019 14:43

History, 27.10.2019 14:43

Mathematics, 27.10.2019 14:43

Health, 27.10.2019 14:43



English, 27.10.2019 14:43

Biology, 27.10.2019 14:43

Geography, 27.10.2019 14:43

Chemistry, 27.10.2019 14:43


French, 27.10.2019 14:43

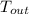 = 37 + 273 = 310 K
= 37 + 273 = 310 K = 13 + 273 = 286 K
= 13 + 273 = 286 K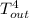 -
- 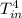 )
)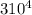 -
- 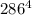 ) = 360.7 J/s
) = 360.7 J/s

