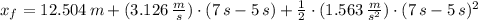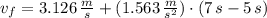Physics, 10.03.2020 08:41 artiomtyler007
A hockey puck with mass 0.160 kg is at rest at the origin (x=0) on the horizontal, frictionless surface of the rink. At time t = 0 a player applies a force of 0.250 N to the puck, parallel to the x-axis; he continues to apply this force until t = 2.00s.
What is the position of the puck at t = 2.00s ?
In this case what is the speed of the puck?
If the same force is again applied at t = 5.00s , what is the position of the puck at t = 7.00s ?
In this case what is the speed of the puck?

Answers: 3


Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 13:30
A2 µc charge q1 and a 2 µc charge q2 are 0.3 m from the x-axis. a 4 µc charge q3 is 0.4 m from the y-axis. the distances d13 and d23 are 0.5 m. find the magnitude and direction of the resulting vector r. round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 12:50
Arunner is jogging at a steady 3.6 km/hr. when the runner is 2.9 km from the finish line, a bird begins flying from the runner to the finish line at 14.4 km/hr (4 times as fast as the runner). when the bird reaches the finish line, it turns around and flies back to the runner. even though the bird is a dodo, we will assume that it occupies only one point in space, i.e., a zero-length bird. how far does the bird travel? (b) after this first encounter, the bird then turns around and flies from the runner back to the finish line, turns around again and flies back to the runner. the bird repeats the back and forth trips until the runner reaches the finish line. how far does the bird travel from the beginning? (i.e. include the distance traveled to the first encounter)
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 23:00
Acommon technique in analysis of scientific data is normalization. the purpose of normalizing data is to eliminate irrelevant constants that can obscure the salient features of the data. the goal of this experiment is to test the hypothesis that the flux of light decreases as the square of the distance from the source. in this case, the absolute value of the voltage measured by the photometer is irrelevant; only the relative value conveys useful information. suppose that in part 2.2.2 of the experiment, students obtain a signal value of 162 mv at a distance of 4 cm and a value of 86 mv at a distance of 5.7 cm. normalize the students' data to the value obtained at 4 cm. (divide the signal value by 162.) then calculate the theoretically expected (normalized) value at 5.7 cm.
Answers: 2

Physics, 23.06.2019 01:30
The amount of potential energy possessed by an elevated object is equal to
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
A hockey puck with mass 0.160 kg is at rest at the origin (x=0) on the horizontal, frictionless surf...
Questions

Business, 01.09.2021 14:00


Physics, 01.09.2021 14:00

English, 01.09.2021 14:00


Mathematics, 01.09.2021 14:00

Mathematics, 01.09.2021 14:00


Chemistry, 01.09.2021 14:00

Mathematics, 01.09.2021 14:00

Mathematics, 01.09.2021 14:00


Mathematics, 01.09.2021 14:00

Mathematics, 01.09.2021 14:00




Physics, 01.09.2021 14:00

Mathematics, 01.09.2021 14:00

Mathematics, 01.09.2021 14:00

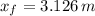 , b)
, b) 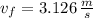 , c)
, c) 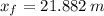 , d)
, d) 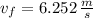
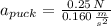
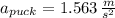
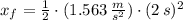
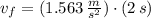
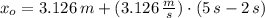
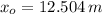
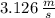 .
.