
Physics, 18.02.2020 02:52 lexidecker243
Earthquakes are essentially sound waves—called seismic waves—traveling through the earth. Because the earth is solid, it can support both longitudinal and transverse seismic waves. The speed of longitudinal waves, called P waves, is 8000 m/s. Transverse waves, called S waves, travel at a slower 4500 m/s. A seismograph records the two waves from a distant earthquake. The S wave arrives 2.0 min after the P wave. Assume that the waves travel in straight lines, although actual seismic waves follow more complex routes. If the S wave arrives 2.3 min after the P wave, how far away was the earthquake?

Answers: 1


Another question on Physics


Physics, 22.06.2019 15:10
Auniform crate c with mass mc is being transported to the left by a forklift with a constant speed v1. what is the magnitude of the angular momentum of the crate about point a, that is, the point of contact between the front tire of the forklift and the ground
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 18:30
Adolphin emits ultrasound at 100khz and uses the timing of reflections to determine the position of objects in the water. part a what is the wavelength of this ultrasound? assume that temperature of water is 20 degrees c. answer in cm
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 21:00
Which of the the following are examples of projectile motion of both projectile motion and two dimensional motion
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Earthquakes are essentially sound waves—called seismic waves—traveling through the earth. Because th...
Questions


Mathematics, 30.09.2019 21:00


Mathematics, 30.09.2019 21:00




Mathematics, 30.09.2019 21:00


Mathematics, 30.09.2019 21:00

Spanish, 30.09.2019 21:00



Business, 30.09.2019 21:00


Chemistry, 30.09.2019 21:00




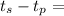 Δt
Δt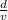 we rewrite the formula as
we rewrite the formula as 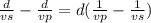 =Δt
=Δt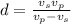 *Δt
*Δt

