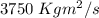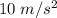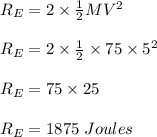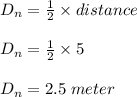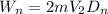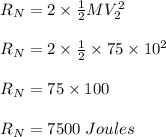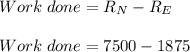Physics, 12.08.2019 22:10 gabrieljerron
Two astronauts, each having a mass of 75.0 kg, are connected by a 10.0-m rope of negligible mass. they are isolated in space, orbiting their center of mass at speeds of 5.00 m/s. treating the astronauts as particles, calculate (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system and (b) the rotational energy of the system. by pulling on the rope, one of the astronauts shortens the distance between them to 5.00 m. (c) what is the new angular momentum of the system? (d) what are the astronauts’ new speeds? (e) what is the new rotational energy of the system? (f) how much work does the astronaut do in shortening the rope?

Answers: 2


Another question on Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 03:00
1. a net force of 100 newton’s is applied to a wagon for 5 seconds. this causes the wagon to undergo a change in momentum of
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 08:00
A0.580-kg rock is tied to the end of a string and is swung in a circle with a radius of 0.500 meters. the velocity of the rock is 4.50 m/s. what is the centripetal force acting on the rock? 15.5 n 5.22 n 69.8 n 23.5 n
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 12:00
In which of the following would the particles move most rapidly? a. ice at -20 °c b. water at 20 °c c. steam at 110 °c d. boiling water e. ice at 0 °c
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 15:30
To understand the behavior of the electric field at the surface of a conductor, and its relationship to surface charge on the conductor. a conductor is placed in an external electrostatic field. the external field is uniform before the conductor is placed within it. the conductor is completely isolated from any source of current or charge. part a: which of the following describes the electric field inside this conductor? it is in the same direction as the original external field.it is in the opposite direction from that of the original external field.it has a direction determined entirely by the charge on its surface.it is always zero. part b: the charge density inside the conductor is: 0non-zero; but uniformnon-zero; non-uniforminfinite part c: assume that at some point just outside the surface of the conductor, the electric field has magnitude e and is directed toward the surface of the conductor. what is the charge density η on the surface of the conductor at that point? express your answer in terms of e and ϵ0
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Two astronauts, each having a mass of 75.0 kg, are connected by a 10.0-m rope of negligible mass. th...
Questions

Computers and Technology, 16.02.2020 06:34

Health, 16.02.2020 06:34

Mathematics, 16.02.2020 06:35

Mathematics, 16.02.2020 06:35


Business, 16.02.2020 06:35




Mathematics, 16.02.2020 06:37





Chemistry, 16.02.2020 06:49

English, 16.02.2020 06:49

Mathematics, 16.02.2020 06:50


Mathematics, 16.02.2020 06:50

Mathematics, 16.02.2020 06:50