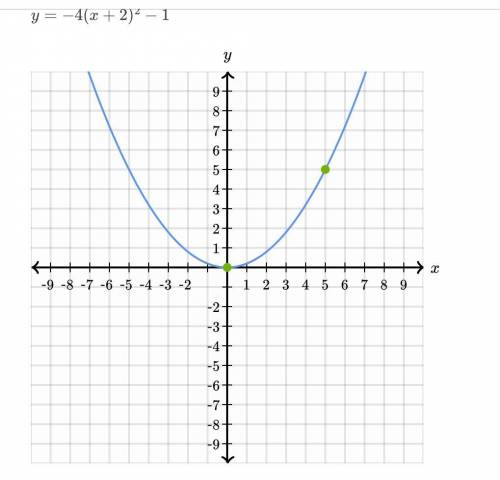
Graph the equation. y = − 4 ( x + 2 ) 2 − 1 y=−4(x+2) 2 −1
...

Mathematics, 01.12.2021 04:00 jordendoctorwho
Graph the equation. y = − 4 ( x + 2 ) 2 − 1 y=−4(x+2) 2 −1

Answers: 3


Another question on Mathematics


Mathematics, 21.06.2019 22:00
Type the correct answer in the box. consider the system of linear equations below. rewrite one of the two equations above in the form ax + by = c, where a, b, and c are constants, so that the sum of the new equation and the unchanged equation from the original system results in an equation in one variable.
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 00:00
I've been working on this for a few days and i just don't understand, it's due in a few hours. you.the direction of a vector is defined as the angle of the vector in relation to a horizontal line. as a standard, this angle is measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. the direction or angle of v in the diagram is α.part a: how can you use trigonometric ratios to calculate the direction α of a general vector v = < x, y> similar to the diagram? part bsuppose that vector v lies in quadrant ii, quadrant iii, or quadrant iv. how can you use trigonometric ratios to calculate the direction (i.e., angle) of the vector in each of these quadrants with respect to the positive x-axis? the angle between the vector and the positive x-axis will be greater than 90 degrees in each case.part cnow try a numerical problem. what is the direction of the vector w = < -1, 6 > ?
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 03:30
On a certain portion of an experiment, a statistical test result yielded a p-value of 0.21. what can you conclude? 2(0.21) = 0.42 < 0.5; the test is not statistically significant. if the null hypothesis is true, one could expect to get a test statistic at least as extreme as that observed 21% of the time, so the test is not statistically significant. 0.21 > 0.05; the test is statistically significant. if the null hypothesis is true, one could expect to get a test statistic at least as extreme as that observed 79% of the time, so the test is not statistically significant. p = 1 - 0.21 = 0.79 > 0.05; the test is statistically significant.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Questions


Mathematics, 26.11.2020 23:10



Physics, 26.11.2020 23:10

History, 26.11.2020 23:10


History, 26.11.2020 23:10


History, 26.11.2020 23:10

Chemistry, 26.11.2020 23:10


Mathematics, 26.11.2020 23:10






Biology, 26.11.2020 23:10

Business, 26.11.2020 23:10



