Mathematics, 08.03.2021 03:00 gmaxgaming88
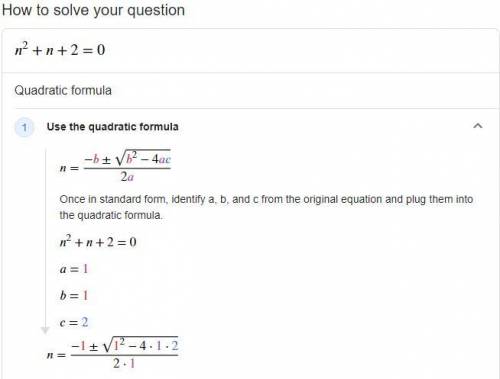
Suppose sigma ∞ to n=1 of (an) converges absolutely.
Define (pn) = max(0, (an)) and (qn) = min(0, (an)).
Then both sigma ∞ to n=1 of (pn) and sigma ∞ to n=1 of (qn) converge.

Answers: 3


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:00
Edger needs 6 cookies and 2 brownies for every 4 plates how many cookies and brownies does he need for 10 plates
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 03:10
Which statement is true about the discontinuities of the function f(x) = x-5/ 3x^2-17x-28
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 07:00
Calculate ∬y da where r is the region between the disks x^2+y^2 < =1 & x^2+(y-1)^2 < =1 show all work. (also explain why you split up the regions)
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 07:00
How do you find the angles inside a triangle with one extirer angle
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Suppose sigma ∞ to n=1 of (an) converges absolutely.
Define (pn) = max(0, (an)) and (qn) = min(0, (...
Questions


Mathematics, 09.04.2021 01:40

Mathematics, 09.04.2021 01:40








Mathematics, 09.04.2021 01:40


Mathematics, 09.04.2021 01:40

Mathematics, 09.04.2021 01:40


Social Studies, 09.04.2021 01:40

Mathematics, 09.04.2021 01:40


Mathematics, 09.04.2021 01:40