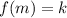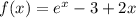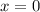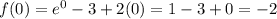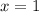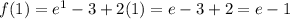Mathematics, 20.10.2020 01:01 marahsenno
Use the Intermediate Value Theorem to show that there is a root of the given equation in the specified interval. ex = 3 − 2x, (0, 1) The equation ex = 3 − 2x is equivalent to the equation f(x) = ex − 3 + 2x = 0. f(x) is continuous on the interval [0, 1], f(0) = , and f(1) = . Since f(0) < 0 < f(1) , there is a number c in (0, 1) such that f(c) = 0 by the Intermediate Value Theorem. Thus, there is a root of the equation ex = 3 − 2x, in the interval (0, 1)

Answers: 3


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 17:20
Match the equivalent expressions. x - 3y + 12 12 - 3y - 2x + x + 2x 3x + 2y - 2x + y + 12 3y + 12 3x + y - 12 4y + 3y + 3x - 6y - 10 - 2 x + 3y + 2x - 3x + 7 + 5 x + 3y + 12 5 + 2y + 7x - 4x + 3y - 17
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:30
Hundred and tens tables to make 430 in five different ways
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 02:00
Aiko jumped rope for 20 min and stopped at 8: 05 when did she start
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 05:30
What is the solution to the system of equations? 10x+3y=8 -9x-y=-20 (11, 1) (1, 11) (–1, 11) (11, –1)'
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Use the Intermediate Value Theorem to show that there is a root of the given equation in the specifi...
Questions

Mathematics, 13.10.2020 14:01


Mathematics, 13.10.2020 14:01

Mathematics, 13.10.2020 14:01

English, 13.10.2020 14:01

Biology, 13.10.2020 14:01




Mathematics, 13.10.2020 14:01





Biology, 13.10.2020 14:01



Mathematics, 13.10.2020 14:01


Mathematics, 13.10.2020 14:01

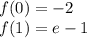
![[a,b]](/tpl/images/0821/6337/f2a2f.png) , and if
, and if 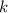 is any number between
is any number between 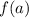 and
and 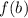 , then there exists a value,
, then there exists a value, 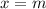 , where
, where 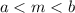 , such that
, such that