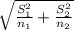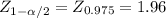Mathematics, 19.06.2020 14:57 LilBrookilyn2701
Suppose we have collected times, in minutes, that it takes volunteers to complete a set of pencil and paper mazes. Volunteers are randomly assigned to one of two groups. Group 1 watch a 5 minute video explaining good strategies for completing the mazes. Group 2 watch a 5 minute video of other people successfully completing the mazes, but with no explanation given.
Researchers are interested in testing against the null hypothesis that there is no difference in population mean times that it takes people to complete mazes after watching either type of video.
There are the summary statistics after collecting data. Note that the sample sizes differ, because some subjects did not follow instructions correctly and so they were not included in the analysis.
x1 = 11.98, x2 = 9.15
s1 = 8.69, s2 = 7.75
n1 = 43, n2 = 52
a. Is this an experimental or observational study?
Observational
Experimental
b. What are the predictor and response variables, and are they categorical or quantitative? (You must get all correct)
Video type is categorical
Finishing time is quantitative
Video type is the response variable
Video type is the predictor variable
Video type is quantitative
Finishing time is categorical
Finishing time is the predictor variable
Finishing time is the response variable
How should the null hypothesis be written?
H0: x1 - x2 = 0
H0: μ1 - μ2 = 5
H0: μ = 0
H0: x = 5
H0: x1 - x2 = 5
H0: μ1 - μ2 = 0
(for the following calculations, round to 2 decimal places)
c. Calculate the standard error of x1 - x2:
d. Calculate the approximate 95% CI for μ1 - μ2: to
e. The result of the hypothesis test is:
We do not have evidence that there is a difference in population means, because the null value is inside the 95% CI.
We do not have evidence that there is a difference in population means, because the null value is outside the 95% CI.
We have evidence that there is a difference in population means, because the null value is inside the 95% CI.
We have evidence that there is a difference in population means, because the null value is outside the 95% CI.
f. What kind of error is it *possible* that we have made?
1. It is possible that we made a Type I error, because this is when you reject a false null hypothesis.
2. It is possible that we made a Type I error, because this is when you fail to reject a false null hypothesis.
3. It is possible that we made a Type I error, because this is when you reject a true null hypothesis.
4. It is possible that we made a Type I error, because this is when you fail to reject a true null hypothesis.
5. It is possible that we made a Type II error, because this is when you reject a false null hypothesis.
6. It is possible that we made a Type II error, because this is when you fail to reject a false null hypothesis.
7. It is possible that we made a Type II error, because this is when you reject a true null hypothesis.
8. It is possible that we made a Type II error, because this is when you fail to reject a true null hypothesis.

Answers: 1


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:00
Aball is dropped from a height of 10m above the ground. it bounce to 90% of its previous height on each bounce. what is the approximate height that the ball bounce to the fourth bounce?
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 21:00
Rewrite the following quadratic functions in intercept or factored form. show your work. f(t) = 20t^2 + 14t - 12
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 21:00
You buy five cds at a sale for $5.95 each. write an expression for the total cost of the cds.then use the distributive property and mental math to evaluate the expression.
Answers: 2

You know the right answer?
Suppose we have collected times, in minutes, that it takes volunteers to complete a set of pencil an...
Questions

Mathematics, 30.06.2021 01:00

Social Studies, 30.06.2021 01:00


Physics, 30.06.2021 01:00

World Languages, 30.06.2021 01:00


History, 30.06.2021 01:00


Mathematics, 30.06.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 30.06.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 30.06.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 30.06.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 30.06.2021 01:00




World Languages, 30.06.2021 01:00



Mathematics, 30.06.2021 01:00

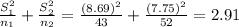
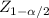 *
*