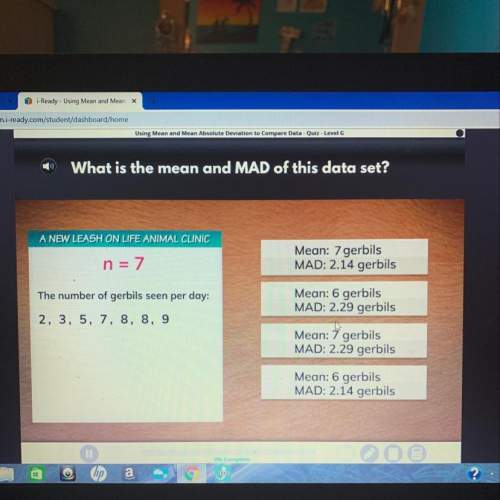
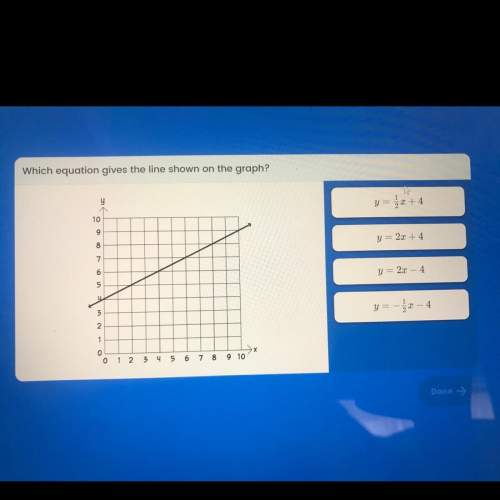
Mathematics, 22.04.2020 00:08 ivethzurita0425
Consider a rotation T (x) = Ax- in R3. (That is, A is an orthogonal 3 × 3 matrix with determinant 1.) Show that T has a nonzero fixed point [i. e., a vector v- with T (v) -= v]. This result is known as Euler’s theorem, after the great Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler (1707–1783). Hint: Consider the characteristic polyno- mial fA(λ). Pay attention to the intercepts with both axes. Use Theorem 7.1.4.

Answers: 1


Another question on Mathematics


Mathematics, 21.06.2019 17:30
Arefrigeration system at your company uses temperature sensors fixed to read celsius (°c) values, but the system operators in your control room understand only the fahrenheit scale. you have been asked to make a fahrenheit (°f) label for the high temperature alarm, which is set to ring whenever the system temperature rises above –10°c. what fahrenheit value should you write on the label
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:00
In a graph with several intervals o data how does a constant interval appear? what type of scenario produces a constant interval?
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:00
The table shows the age and finish time of ten runners in a half marathon. identify the outlier in this data set. drag into the table the ordered pair of the outlier and a reason why that point is an outlier.
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Consider a rotation T (x) = Ax- in R3. (That is, A is an orthogonal 3 × 3 matrix with determinant 1....
Questions

History, 03.01.2020 02:31




Social Studies, 03.01.2020 02:31



Computers and Technology, 03.01.2020 02:31







Business, 03.01.2020 02:31


Chemistry, 03.01.2020 02:31


Computers and Technology, 03.01.2020 02:31

Social Studies, 03.01.2020 02:31