Mathematics, 21.04.2020 01:38 Gabilop
A diagnostic test has a probability 0.95 of giving a positive result when applied to a person suffering from a certain disease, and a probability 0.10 of giving a (false) positive when applied to a non-sufferer. It is estimated that 0.5 % of the population are sufferers. Suppose that the test is now administered to a person about whom we have no relevant information relating to the disease (apart from the fact that he/she comes from this population). Calculate the following probabilities:
a. that the test result will be positive
b. that, given a positive result, the person is a sufferer
c. that, given a negative result, the person is a non-sufferer
d. that the person will be misclassified

Answers: 1


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:00
Manny bought 12 pounds of vegetables at the supermarket. 75% of the vegetables were on sale. how many pounds of vegetables were not on sale? 98 points : )
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:30
What is coefficient of the term of degree of degree 5 in the polynomial below
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 19:00
What is the explicit formula for this sequence? -7, -4, -1, 2, a.) an = 8 + (b - 1)3 b.) an = -7 + (n - 1)3 c.) an = 3 + (n -1) (-7) d.) an = -7 + (n - )
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:00
Find the value of x. give reasons to justify your solutions! l, m ∈ kn
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
A diagnostic test has a probability 0.95 of giving a positive result when applied to a person suffer...
Questions

Mathematics, 27.01.2020 18:31




Social Studies, 27.01.2020 18:31



History, 27.01.2020 18:31

Mathematics, 27.01.2020 18:31

Business, 27.01.2020 18:31

Social Studies, 27.01.2020 18:31




Mathematics, 27.01.2020 18:31

Mathematics, 27.01.2020 18:31

Social Studies, 27.01.2020 18:31

Mathematics, 27.01.2020 18:31

Mathematics, 27.01.2020 18:31

Biology, 27.01.2020 18:31

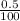 ) + ( 0.10 ×
) + ( 0.10 × 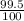 )
)