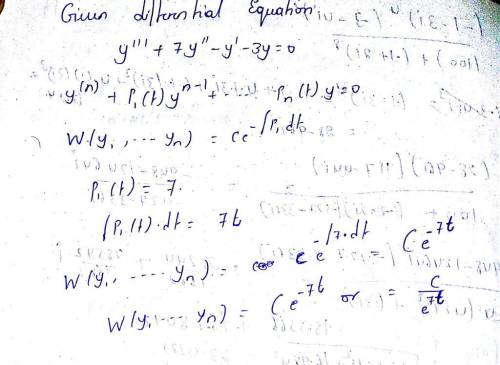Mathematics, 15.04.2020 22:06 shaniahharrisoov3lqv
For the differential equation y(n)+p1(t)y(n−1)+ ... +pn(t)y=0 with solutions y1, ..., yn Abel's formula for the Wronskian is W(y1,...,yn)(t)=Ce−∫p1(t)dt. Use Abel's formula to find the Wronskian of a fundamental set of solutions of the differential equation y′′′+7y′′−y′−3y=0.

Answers: 2


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 14:50
Question 101 points)which equation in slope-intercept form represents the line that passes through (5, 1) and(-4,7)
Answers: 1


Mathematics, 22.06.2019 04:30
Acertain company's main source of income is a mobile app. the company's annual profit (in millions of dollars) as a function of the app's price (in dollars) is modeled by p(x)=-2(x-3)(x-11)p(x)=−2(x−3)(x−11) which app prices will result in \$0$0 annual profit? enter the lower price first.
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 05:00
Allen's goal is to have between 1,500 and 1,600 bottles in his collection. write and solve a compound inequality to determine the number of weeks it will take allen to reach his goal. show your work. *
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
For the differential equation y(n)+p1(t)y(n−1)+ ... +pn(t)y=0 with solutions y1, ..., yn Abel's form...
Questions

Mathematics, 25.06.2019 02:30

English, 25.06.2019 02:30

Mathematics, 25.06.2019 02:30



Mathematics, 25.06.2019 02:30


Social Studies, 25.06.2019 02:30

Social Studies, 25.06.2019 02:30

Mathematics, 25.06.2019 02:30

History, 25.06.2019 02:30


Chemistry, 25.06.2019 02:30

Mathematics, 25.06.2019 02:30

Mathematics, 25.06.2019 02:30


Chemistry, 25.06.2019 02:30

Mathematics, 25.06.2019 02:30