
Chemistry, 04.08.2019 22:30 kyliemorgan8623
Consider the following three-step representation of a reaction mechanism. step 1: a + b mc016-1.jpg ab (fast) and the rate = k[a][b] step 2: ab + b mc016-2.jpg ab2 (slow) and the rate = k[ab][b] step 3: ab2 + b mc016-3.jpg ab3 (fast) and the rate = k[ab2][b] overall: a + 3b mc016-4.jpg ab3 and the rate = k[a][b]2 which explains why the rate law for the overall equation is not the same as the rate equation for the rate-determining step?

Answers: 2


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 06:30
What is the correct term for living the most sustainable life you can within your current circumstances?
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 17:30
Observation and experimentation have led many scientists to accept a theory about the origin of the universe. this theory is called the big bang theory. scientific evidence collected and observed by scientists around the world suggests that the universe is ever expanding from a hot and dense initial state. what makes this a scientific theory? (2 points)
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 22:30
Molecular iodine, i2(g), dissociates into iodine atoms at 625 k with a first-order rate constant of 0.271 s−1. part a part complete what is the half-life for this reaction?
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 23.06.2019 10:30
Chemical bonds result from the interaction of the from two or more atoms. a. protons b. electrons c. neutrons d. nuclei
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Consider the following three-step representation of a reaction mechanism. step 1: a + b mc016-1.jpg...
Questions


Mathematics, 09.02.2021 06:40

Mathematics, 09.02.2021 06:40


Geography, 09.02.2021 06:40

Chemistry, 09.02.2021 06:40




Mathematics, 09.02.2021 06:40

English, 09.02.2021 06:40


Mathematics, 09.02.2021 06:40



Mathematics, 09.02.2021 06:40

Mathematics, 09.02.2021 06:40

Advanced Placement (AP), 09.02.2021 06:40

Mathematics, 09.02.2021 06:40

History, 09.02.2021 06:40

![A+B\rightleftharpoons AB(fast)\\Rate=K[A][B]](/tpl/images/0171/0396/8b588.png)
![AB+B\rightarrow AB_2(slow)\\Rate=K[AB][B]](/tpl/images/0171/0396/fb2ef.png)
![AB_2+B\rightleftharpoons AB_3(fast)\\Rate=K[AB_2][B]](/tpl/images/0171/0396/ac6cb.png)
![Rate=K[A][B]^2](/tpl/images/0171/0396/92d0b.png)
![Rate=K[AB][B]](/tpl/images/0171/0396/058ce.png) ...........(A)
...........(A)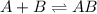
![K=\frac{[AB]}{[A][B]}](/tpl/images/0171/0396/6ec78.png)
![[AB]=K[A][B]](/tpl/images/0171/0396/ad806.png)
![Rate=KK[A][B][B]](/tpl/images/0171/0396/3919b.png)
![Rate=K'[A][B]^2](/tpl/images/0171/0396/8db87.png)


