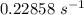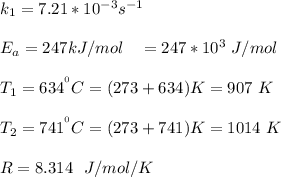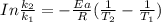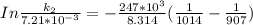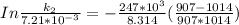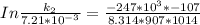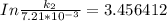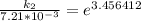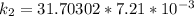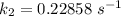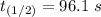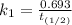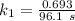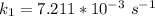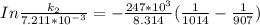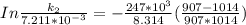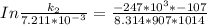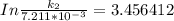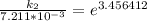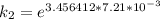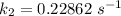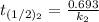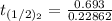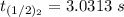The rate constant of the elementary reaction C2H5CN(g) → CH2CHCN(g) + H2(g) is k = 7.21×10-3 s-1 at 634 °C, and the reaction has an activation energy of 247 kJ/mol. (a) Compute the rate constant of the reaction at a temperature of 741 °C. s-1 (b) At a temperature of 634 °C, 96.1 s is required for half of the C2H5CN originally present to be consume. How long will it take to consume half of the reactant if an identical experiment is performed at 741 °C? (Enter numbers as numbers, no units. For example, 300 minutes would be 300. For letters, enter A, B, or C. Enter numbers in scientific notation using e# format. For example 1.43×10-4 would be 1.43e-4.)

Answers: 2


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 09:00
Ineed to find the answer of this question because i dont understand it
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 14:30
Amixture that has two or more substances that are spread out evenly is called a. compound b. heterogeneous c. substance d. homogeneous
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 15:20
Select the most likely product for this reaction: koh(aq) + co2(g) – ? k2co3(aq) + h2o(1) k(s) + h2(g) + o2(g) k(s) + co3(9) +h2
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 15:30
Light waves can move through , but they travel fastest when they move through a(n) .
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
The rate constant of the elementary reaction C2H5CN(g) → CH2CHCN(g) + H2(g) is k = 7.21×10-3 s-1 at...
Questions

Mathematics, 28.01.2020 03:31




Computers and Technology, 28.01.2020 03:31

Biology, 28.01.2020 03:31

Social Studies, 28.01.2020 03:31

Mathematics, 28.01.2020 03:31


Mathematics, 28.01.2020 03:31



History, 28.01.2020 03:31


Biology, 28.01.2020 03:31




English, 28.01.2020 03:31

Mathematics, 28.01.2020 03:31