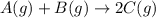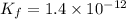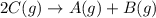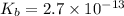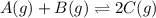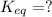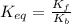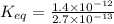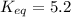Chemistry, 30.03.2020 19:28 starlightmoon213
Find the equilibrium constant for the reaction: A(g) + B(g) ⇌ 2C(g) at 25°C when k equals 1.4 × 10-12 M-1s-1 for the reaction: A(g) + B(g) → 2C(g) at 25°C and k equals 2.7 × 10-13 M-1s-1 for the reaction: 2C(g) → A(g) + B(g) at 25°C.

Answers: 1


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 09:20
Explain that newton first law,second law and third law of motion?
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 13:30
Which is true of a liquid? it has a definite volume but not a definite mass.it has a definite mass but not a definite volume.it has a definite volume but not a definite shape.it has a definite shape but not a definite volume.
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 14:00
How does the presence of oxygen affect the chemical pathways used to extract energy from glucose?
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 17:30
Aroller coaster is traveling at 13 mi./s when you purchase a hill that is 400 m long and down the hill exonerate at 4.0 m/s squared what is the final velocity of the posterior found your answer to the nearest number
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Find the equilibrium constant for the reaction: A(g) + B(g) ⇌ 2C(g) at 25°C when k equals 1.4 × 10-1...
Questions


Business, 22.06.2021 14:30

Health, 22.06.2021 14:30

Chemistry, 22.06.2021 14:50

English, 22.06.2021 14:50

Engineering, 22.06.2021 14:50



Health, 22.06.2021 14:50

English, 22.06.2021 14:50


Mathematics, 22.06.2021 14:50

Social Studies, 22.06.2021 14:50

English, 22.06.2021 14:50



English, 22.06.2021 14:50


Mathematics, 22.06.2021 14:50