Background info:
the standard enthalpy of formation (δh∘f) is the enthalpy change that occurs...

Chemistry, 19.08.2019 10:30 terryonsavage543
Background info:
the standard enthalpy of formation (δh∘f) is the enthalpy change that occurs when exactly1 mol of a compound is formed from its constituent elements under standard conditions. the standard conditions are 1 atm pressure, a temperature of 25 ∘c , and all the species present at a concentration of 1 m . a "standard enthalpies of formation table" containing δh∘f values might look something like this: substanceδh∘fh(g)218 kj/molh2(g)0 kj/molba(s)0 kj/molba2+(aq)−538.4 kj/molc(g)71 kj/molc(s)0 kj/moln(g)473 kj/molo2(g)0 kj/molo(g)249 kj/mols2(g)129 kj/mol
question:
what is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction used to calculate δh∘f of baco3(s)? if fractional coefficients are required, enter them as a fraction (i. e. 1/3). indicate the physical states using the abbreviation (s), (l), or (g) for solid, liquid, or gas, respectively. use (aq) for aqueous solution.
express answer as a chemical equation. explain for me !

Answers: 1


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 20:00
2h2s + 3o2 2so2 + 2h2o which option gives the correct mole ratios? h2s: so2 = 2: 2 and o2: h2o = 3: 2 h2s: so2 = 2: 3 and o2: h2o = 3: 2 h2s: so2 = 4: 4 and o2: h2o = 5: 4 h2s: so2 = 4: 6 and o2: h2o = 4: 4
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 06:00
Oxidation-reduction reactions (often called "redox" for short) are reactions that involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another. oxidation states, or oxidation numbers, allow chemists to keep track of these electron transfers. in general, one element will lose electrons (oxidation), with the result that it will increase in oxidation number, and another element will gain electrons (reduction), thereby decreasing in oxidation number. the species that is oxidized is called the reducing agent or reductant. the species that is reduced is called the oxidizing agent or oxidant. to sum up: oxidation = increase in oxidation state = loss of electrons = reducing agent reduction = decrease in oxidation state = gain of electrons = oxidizing agent part a which element is oxidized in this reaction? fe2o3+3co→2fe+3co2 enter the elemental symbol. view available hint(s) is oxidized part b which element is reduced in this reaction? 2hcl+2kmno4+3h2c2o4→6co2+2mno2+2kcl+4h2o enter the elemental symbol. view available hint(s) is reduced
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 17:00
The arrangement of particles is most ordered in a sample of
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 19:30
Use the periodic table to find the molar mass of each element. molar mass h = g/mol molar mass s = g/mol molar mass o = g/mol
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Questions

Mathematics, 26.07.2019 16:40

Social Studies, 26.07.2019 16:40


Social Studies, 26.07.2019 16:40

Mathematics, 26.07.2019 16:40




Health, 26.07.2019 16:40


English, 26.07.2019 16:40


English, 26.07.2019 16:40


History, 26.07.2019 16:40


History, 26.07.2019 16:40


English, 26.07.2019 16:40

History, 26.07.2019 16:40

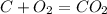
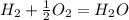
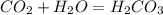
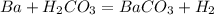
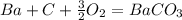 , using hydrogen as a catalyst.
, using hydrogen as a catalyst.

