
Biology, 25.03.2021 22:10 starfox5454
Use the key to identify the fish.
Start by reading the first pair of statements, then decide which of the two statements describes your specimen. The statement you choose will either give you the identity of your fish or direct you to another numbered pair of statements.
Record each number from the key that you use to identify each organism in the Numbers from the key column in Table 1.
When you have finally identified your fish, record its scientific and common names in the appropriate columns of Table 1.
Repeat steps 1 through 3 for additional specimens. An example has been completed for you.

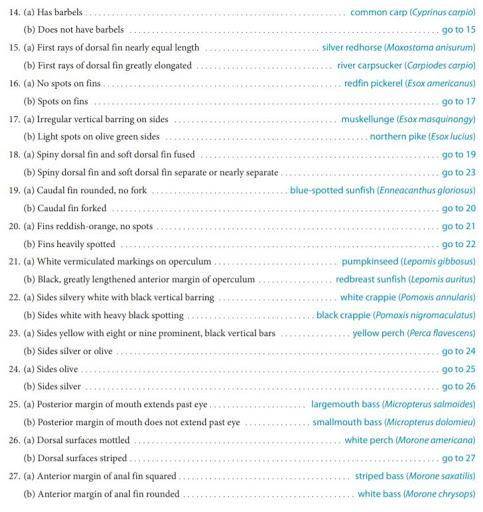
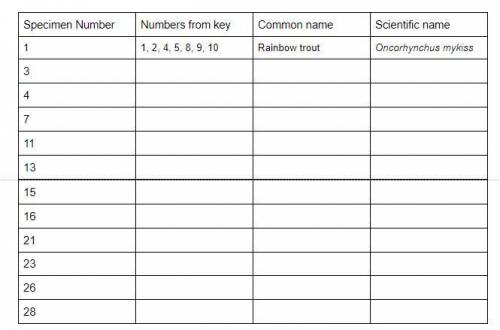

Answers: 1


Another question on Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 20:30
Match the descriptions / definitions with the term they best describe 1. three dimensional relationship of the different polypeptide chains in a multisubunit protein or protein complex 2. common folding pattern in proteins in which a linear sequence of amino acids folds into a right-handed coil stabilized by internal hydrogen-bonding between polypeptide backbone atoms. 3. the amino acid sequence of a protein 4. a region on the surface of a protein that can interact with another molecule through noncovalent bonding. 5. three-dimensional arrangement of alpha-helices and beta-sheets within a single polypeptide, typically stabilized by a variety of noncovalent bonds, including ionic and hydrogen bonds, and nonpolar interactions / hydrophobic force. 6. the chain of repeating carbon and nitrogen atoms, linked by peptide bonds, in a protein. 7. common structural motif in proteins in which different sections of the polypeptide chain run alongside each other and are joined together by hydrogen bonding between atoms of the polypeptide backbone. 8. portion of a polypeptide chain that has a discrete tertiary structure of its own and can often fold independently of the rest of the chain 9. regular local folding patterns in a protein, including alpha-helix and beta-sheet a. primary structure b. beta-sheet c. protein d. coiled-coil e. polypeptide backbone f. secondary structure g. side chain h. tertiary structure i. binding site j. alpha-helix k. quaternary structure l. protein domain
Answers: 2


Biology, 22.06.2019 03:30
How can active reading strategies you? o a. they can you get into better physical shape. o b. they can you read fewer science articles. o c. they can you understand what you read. o d. they can you avoid reading altogether.
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 04:30
Which of the following describes a difference when gram-positive bacteria are compared to gram-negative bacteria?
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Use the key to identify the fish.
Start by reading the first pair of statements, then decide which...
Questions





Mathematics, 24.06.2019 02:30

History, 24.06.2019 02:30

History, 24.06.2019 02:30



SAT, 24.06.2019 02:30

Biology, 24.06.2019 02:30



English, 24.06.2019 02:30



History, 24.06.2019 02:30


English, 24.06.2019 02:30



