Biology, 06.05.2020 05:36 ayoismeisalex
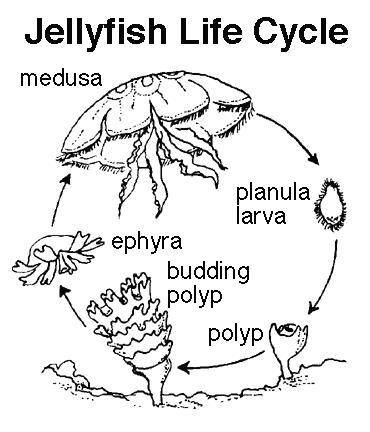
Is a Jellyfish free-swimming for its whole life? Explain why or why not.

Answers: 1


Another question on Biology

Biology, 20.06.2019 18:04
Jerry wants to consume no more than 45% of his calories from carbohydrates. calculate his requirement for calories from carbohydrates based on a 2,500 kcal per day intake.
Answers: 1

Biology, 21.06.2019 13:30
Which of the following choices is not an effective solution to the energy waste related to inefficient lighting? a. using low-pressure sodium lighting sources b. pointing lights on billboards and street signs upward c. placing light sources on time controls d. shielding light to direct it downward
Answers: 1

Biology, 21.06.2019 16:10
Explain why in any given geographical region, women tend to have lighter skins( by 3-4% on average) than men?
Answers: 1

Biology, 21.06.2019 20:30
Match the descriptions / definitions with the term they best describe 1. three dimensional relationship of the different polypeptide chains in a multisubunit protein or protein complex 2. common folding pattern in proteins in which a linear sequence of amino acids folds into a right-handed coil stabilized by internal hydrogen-bonding between polypeptide backbone atoms. 3. the amino acid sequence of a protein 4. a region on the surface of a protein that can interact with another molecule through noncovalent bonding. 5. three-dimensional arrangement of alpha-helices and beta-sheets within a single polypeptide, typically stabilized by a variety of noncovalent bonds, including ionic and hydrogen bonds, and nonpolar interactions / hydrophobic force. 6. the chain of repeating carbon and nitrogen atoms, linked by peptide bonds, in a protein. 7. common structural motif in proteins in which different sections of the polypeptide chain run alongside each other and are joined together by hydrogen bonding between atoms of the polypeptide backbone. 8. portion of a polypeptide chain that has a discrete tertiary structure of its own and can often fold independently of the rest of the chain 9. regular local folding patterns in a protein, including alpha-helix and beta-sheet a. primary structure b. beta-sheet c. protein d. coiled-coil e. polypeptide backbone f. secondary structure g. side chain h. tertiary structure i. binding site j. alpha-helix k. quaternary structure l. protein domain
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Is a Jellyfish free-swimming for its whole life? Explain why or why not....
Questions



Mathematics, 15.04.2021 01:00



Mathematics, 15.04.2021 01:00

History, 15.04.2021 01:00


Computers and Technology, 15.04.2021 01:00

History, 15.04.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 15.04.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 15.04.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 15.04.2021 01:00

Computers and Technology, 15.04.2021 01:00

English, 15.04.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 15.04.2021 01:00

English, 15.04.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 15.04.2021 01:00


Mathematics, 15.04.2021 01:00