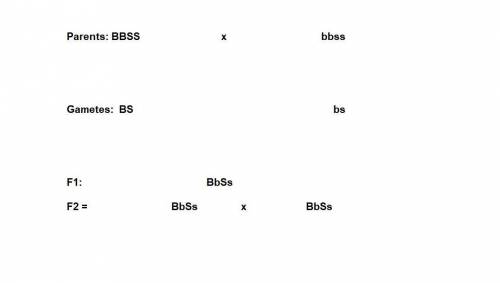
In watermelons, bitter fruit (b) is dominant over sweet fruit (b), and yellow spots (s) are dominant over no spots (s). the genes for these two characteristics assort independently. a homozygous plant that has bitter fruit and yellow spots is crossed with a homozygous plant that has sweet fruit and no spots. the f1 are intercrossed to produce the f2. what will be the phenotypic ratio in the f2?

Answers: 1


Another question on Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 18:40
The study of interaction between living organisms and their enviroment is called (a) phytogeography (b) ecology (c) phytosociology (d) ecosystem
Answers: 3

Biology, 22.06.2019 05:00
(99 points) be serious! how do farts work? how do you fart without it stinking? serious answers only
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 11:00
Match the following terms and definitions. 1. species that are adapted to live in equilibrium at carrying capacity population density 2. population growth that reaches equilibrium and carrying capacity population 3. death rate mortality 4. birth rate k-selected 5. a group of interacting individuals of the same species within the same geographic area natality 6. the number of organisms living in a particular area logistic growth
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 13:00
Suppose you are provided with an actively dividing culture of e. coli bacteria to which radioactive thymine has been added. what would happen if a cell replicates once in the presence of this radioactive base?
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
In watermelons, bitter fruit (b) is dominant over sweet fruit (b), and yellow spots (s) are dominant...
Questions

History, 07.07.2019 16:30




Mathematics, 07.07.2019 16:30

History, 07.07.2019 16:30

Social Studies, 07.07.2019 16:30





History, 07.07.2019 16:30

History, 07.07.2019 16:30







Social Studies, 07.07.2019 16:40